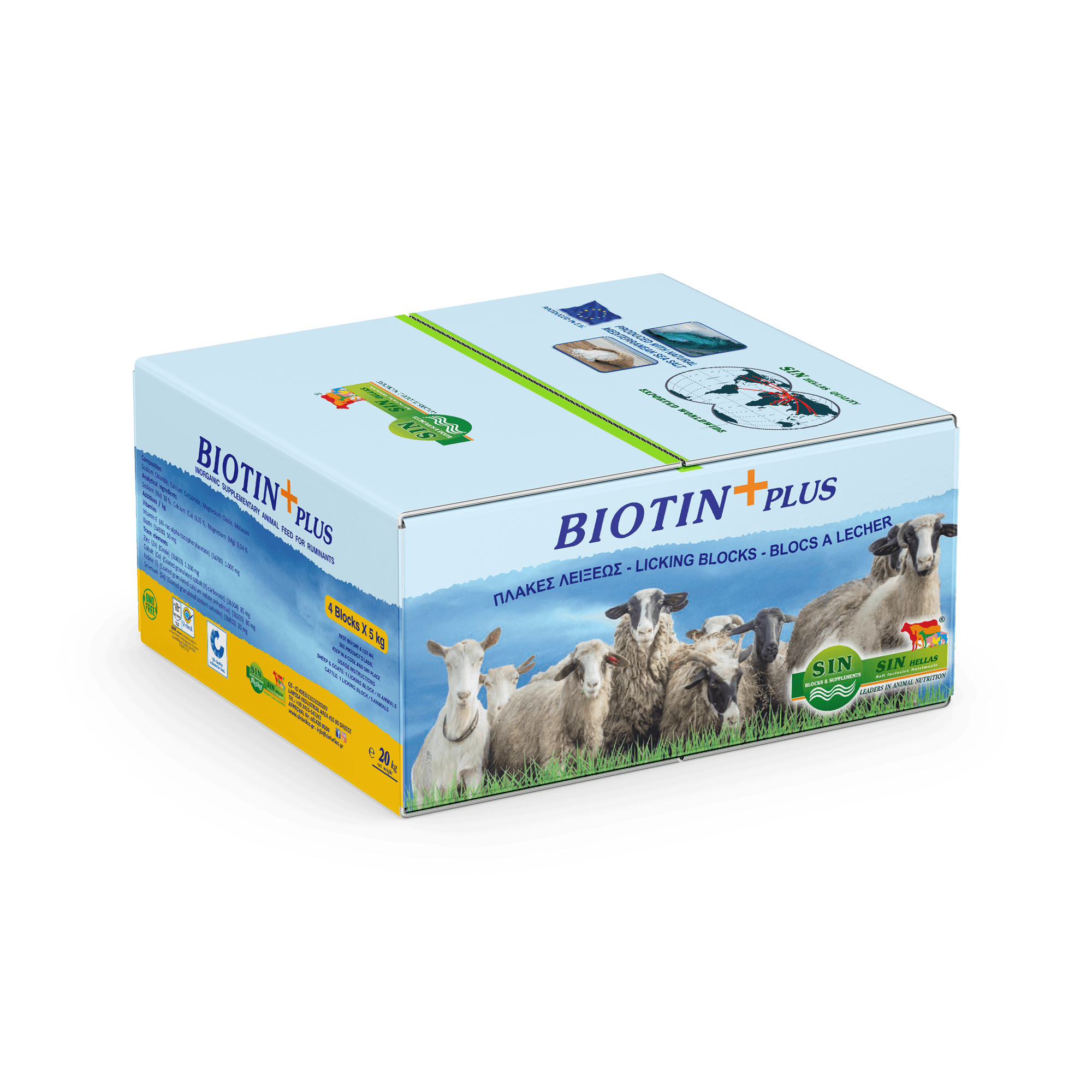
BIOTIN PLUS+
Biotin Licking Blocks
Minerals, Trace Elements & Vitamins



















- An ideal BIOTIN (Vitamin H) & Vitamin E combination with impressive results.
Benefits
- Increased milk production
- Hoof Health Improvement
- Skin Quality improvement
- Protection against mastitis
- Meat and Milk Quality Improvement
- Increased immunity
Nutrition Facts
Analytical Ingredients / %
Sodium (Na)38%
Calcium (Ca)1%
Magnesium (Mg)1%
Minerals mg / Kg
Zinc (Zn)25%
Cobalt (Co)10%
Iodine (I)10%
Selenium (Se)4%
Vitamins IU / Kg
Vitamin E18%
Biotin (Vitamin H)5%
Composition
- Sodium Chloride, Calcium Carbonate, Magnesium Oxide, Molasses (Sugar beet)
What is improving
Vitamin H / Biotin
VITAMIN H / BIOTIN is an essential coenzyme in carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism and it promotes hoof health by improving horn quality. It is involved in conversion of carbohydrate to protein and vice versa, as well as conversion of protein and carbohydrate to fat. Biotin also plays an important role in maintaining normal blood glucose levels from metabolism of protein and fat when the dietary intake of carbohydrate is low.
Magnesium
Magnesium is needed for more than 300 biochemical reactions in the body. It helps to maintain normal nerve and muscle function, supports a healthy immune system, keeps the heartbeat steady, and helps bones remain strong. It also helps adjust blood glucose levels. It aids in the production of energy and protein, improves the digestibility of feed and improves the reproduction.
Selenium
Selenium is a component of glutathione peroxidase, an enzyme for the removal of lipid peroxides. Selenium is very important in fertility and helps muscular development. Se is also a component of two other selenoproteins. The midpiece of sperm requires selenoprotein. Microbes in the rumen replace S with Se in their S-containing amino acid synthesis. They are absorbed in the duodenum as amino acids. White muscle disease and exudative diathesis are two Se deficiency symptoms, which can be treated with both vitamin E and Se. Deficient animals also show liver necrosis. Selenium prevents oxidative damage to tissues by offering an antioxidant action and protects against cell damage.
Iodine
Iodine’s function is as a constituent of thyroxin, a thyroid gland hormone that regulates the basal metabolic rate. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, enhances the iodine uptake by the thyroid gland. Short-term deficiency leads to hypothyroidism, with reduced growth rate and reproductive problems, hair loss, and dry skin. Long-term deficiency leads to goiter. Without iodine, thyroxin cannot be synthesized. This causes the release of TSH, which in turn causes the hypertrophy of the thyroid gland.
Zinc
Zinc is an essential nutrient for animals, functioning in enzyme systems and being involved in protein synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and many other biochemical reactions. A severe zinc deficiency causes numerous pathological changes, including skin parakeratosis, reduced or cessation of growth, general debility, lethargy, and increased susceptibility to infection.
Cobalt
Cobalt has only one known function, which is a constituent of vitamin B12. Cobalt is required for rumen microbes to synthesize vitamin B12. Deficiency symptoms are easily confused with gross malnutrition or starvation.
Calcium
Calcium is the main component of bones and teeth. It has chief metabolic functions in the animal bodies and is also essential for muscle activity, skeleton, blood clotting, nerve transmission and dynamics of enzyme function. Calcium metabolism at calving is one of the most important animal health factors influencing the production, reproduction and feed conversion efficiency as it plays a major role in the absorption of nutrients (modification of the cell permeability) .
Vitamin E
Vitamin E has been shown to be essential for integrity and optimum function of reproductive, muscular, circulatory, nervous, and immune systems. One of the most important functions is its role as an intercellular and intracellular antioxidant. Vitamin E is part of the body’s intracellular defense against the adverse effects of reactive oxygen and free radicals that initiate oxidation of unsaturated phospholipids and critical sulfhydryl groups.
Case Study
1The Role Of Biotin In Animals' Nutrition
Suitable for
Sheep, Goats, Dairy Cows, Dry Cows, Cattle / Beef, Horse, Camel, Wild / Prey
Available Colors
Packaging

Box of 8pcs x 3kg
3kg blocks wrapped in plastic film in box of 8pcs x 3kg

Box of 4pcs x 5kg
5kg blocks wrapped in plastic film in box of 4pcs x 5kg

10kg block
Individually shrink wrapped 10kg block with handling strap.
Related Products
Cookies
To ensure the proper functioning of the website, we sometimes place small data files on your computer, the so-called "cookies". Most major websites do the same.
Accept
Change Settings
Cookie Box Settings
Cookie Box Settings
Privacy settings
Decide which cookies you want to allow.
You can change these settings at any time. However, this can result in some functions no longer being available. For information on deleting the cookies, please consult your browser’s help function.
Learn more about the cookies we use.With the slider, you can enable or disable different types of cookies:
This website will:
- Essential: Remember your cookie permission setting
- Essential: Allow session cookies
- Essential: Gather information you input into a contact forms, newsletter and other forms across all pages
- Essential: Keep track of what you input in a shopping cart
- Essential: Authenticate that you are logged into your user account
- Essential: Remember language version you selected
This website won't:
- Remember your login details
- Functionality: Remember social media settings
- Functionality: Remember selected region and country
- Analytics: Keep track of your visited pages and interaction taken
- Analytics: Keep track about your location and region based on your IP number
- Analytics: Keep track of the time spent on each page
- Analytics: Increase the data quality of the statistics functions
- Advertising: Tailor information and advertising to your interests based on e.g. the content you have visited before. (Currently we do not use targeting or targeting cookies.
- Advertising: Gather personally identifiable information such as name and location
This website will:
- Essential: Remember your cookie permission setting
- Essential: Allow session cookies
- Essential: Gather information you input into a contact forms, newsletter and other forms across all pages
- Essential: Keep track of what you input in a shopping cart
- Essential: Authenticate that you are logged into your user account
- Essential: Remember language version you selected
- Functionality: Remember social media settings
- Functionality: Remember selected region and country
This website won't:
- Remember your login details
- Analytics: Keep track of your visited pages and interaction taken
- Analytics: Keep track about your location and region based on your IP number
- Analytics: Keep track of the time spent on each page
- Analytics: Increase the data quality of the statistics functions
- Advertising: Tailor information and advertising to your interests based on e.g. the content you have visited before. (Currently we do not use targeting or targeting cookies.
- Advertising: Gather personally identifiable information such as name and location
This website will:
- Essential: Remember your cookie permission setting
- Essential: Allow session cookies
- Essential: Gather information you input into a contact forms, newsletter and other forms across all pages
- Essential: Keep track of what you input in a shopping cart
- Essential: Authenticate that you are logged into your user account
- Essential: Remember language version you selected
- Functionality: Remember social media settingsl Functionality: Remember selected region and country
- Analytics: Keep track of your visited pages and interaction taken
- Analytics: Keep track about your location and region based on your IP number
- Analytics: Keep track of the time spent on each page
- Analytics: Increase the data quality of the statistics functions
This website won't:
- Remember your login details
- Advertising: Use information for tailored advertising with third parties
- Advertising: Allow you to connect to social sites
- Advertising: Identify device you are using
- Advertising: Gather personally identifiable information such as name and location
This website will:
- Essential: Remember your cookie permission setting
- Essential: Allow session cookies
- Essential: Gather information you input into a contact forms, newsletter and other forms across all pages
- Essential: Keep track of what you input in a shopping cart
- Essential: Authenticate that you are logged into your user account
- Essential: Remember language version you selected
- Functionality: Remember social media settingsl Functionality: Remember selected region and country
- Analytics: Keep track of your visited pages and interaction taken
- Analytics: Keep track about your location and region based on your IP number
- Analytics: Keep track of the time spent on each page
- Analytics: Increase the data quality of the statistics functions
- Advertising: Use information for tailored advertising with third parties
- Advertising: Allow you to connect to social sitesl Advertising: Identify device you are using
- Advertising: Gather personally identifiable information such as name and location
This website won't:
- Remember your login details