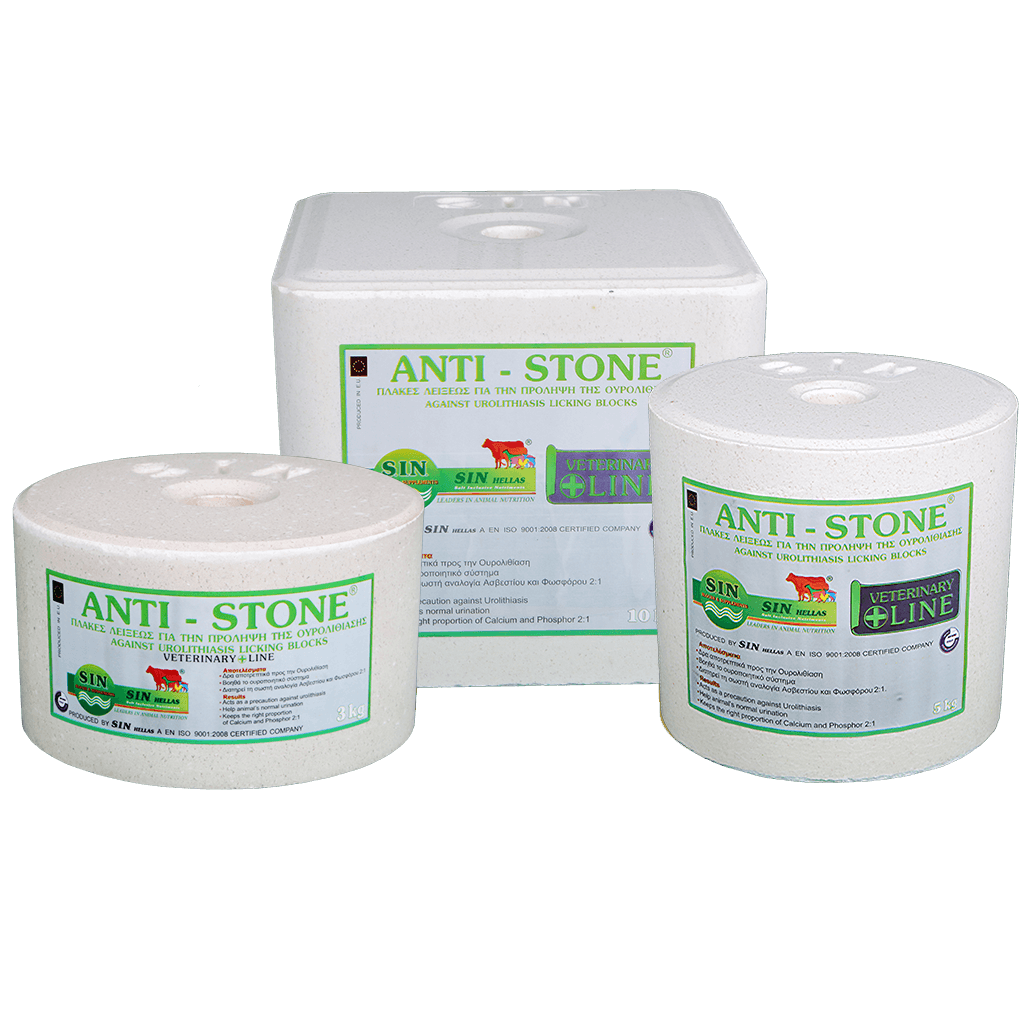
ANTI - STONE
Urolithiasis preventing Licking Block
Minerals , Elements & Trace Elements






















- Acts as a precaution against urolithiasis
- Helps animal' s normal urination
- Keeps the right proportion of calcium & phosphor 2:1
Urolothiasasis Symptoms
Urolithiasasis can affect all ruminats. Most likely are affected the animals which are fed with concentrated foods, like for example the meat production animals. To the affected by the illness animals, UROLITHS (STONE) are created into the kidneys and into the bladder with symptoms such as urination difficulty and belly pains. The uroliths usually are createdby Magnesium Phospate. When the urethral obstruction is not full, the animal hasdifficulty in urinating and in urine there is a small amount of blood, but when the obstruction is complete then the bladder or the urethra breaks, the belly swells and animal dies. The metabolic disease is mainly due to the animal' s diet with large amounts of concentrated food or in the wrong proportion of minerals such aw Calcium, Phosphorus or Magnesium.
Precautions Against Ourolithiasis
- The proportion of minerals such as Calcium and Phosphorus should ideally be kept as 2:1. The Dicalcium Phosphate does not cause Urolithiasis while the Sodium Phosphate acts in favor of it
- Inorganic compounds such aw Ammonium Chloride, dissolve stones (UROLITHS) contributing in this way in the preventation against the disease
- Sufficient quantity of clear, fresh and of good chemical analysis watering
- Addition of Vitamin A to the ration protects from barking of the mucosal cells which form the first nucleus of uroliths
Nutrition Facts
Analytical Ingredients / %
Sodium (Na)36%
Ammonium Chloride (NH4CL)5%
Calcium (Ca)1%
Magnesium (Mg)1%
Phosphor (P)1%
Minerals mg / Kg
Iron (Fe) (Sulphate monohydrate (II) (3b103)20%
Manganese (Mn) (Oxide) (3b502)15%
Zinc (Zn) (Oxide) (3b603)13%
Iodine (I) (Coated granulated calcium iodate anhydrous) (3b203)10%
Cobalt (Co) (Coated granulated cobalt (II) carbonate) (3b304)4%
Selenium (Se) (Coated granulated sodium selenite) (3b802)2%
Vitamins IU / Kg
Vitamin A (Retinyl acetate) (3a672a)50%
Vitamin D3 (Cholicalciferol) (3a671)25%
Vitamin E (All-rac-alpha-tocopherylacetate) (3a700)5%
Composition
Sodium Chloride, Ammonium Chloride, Dicalcium Phosphate, Calcium Carbonate, Magnesium Oxide, Molasses (Sugar beet)
What is improving
Zinc
Magnesium
Calcium
Iron
Phosphorus
Vitamin A
Vitamin D3
Vitamin E
Suitable for
Sheep, Goats, Dairy Cows, Dry Cows, Cattle / Beef, Horse
Available Colors
Packaging

Box of 8pcs x 3kg
3kg blocks wrapped in plastic film in box of 8pcs x 3kg

Box of 4pcs x 5kg
5kg blocks wrapped in plastic film in box of 4pcs x 5kg

10kg block
Individually shrink wrapped 10kg block with handling strap.